Cartilage at the tip of the nose. Bone is another type of supporting connective tissue.

Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
Adipose is another type of supporting connective tissue that.
. Thus the correct answer is option D. D It is found in young infants. A Hyaline b Elastic c Fibrocartilage.
D It is found in young infants. Cartilage is found throughout the human body in areas such as the joints nose airway intervertebral discs of the spine and the ear. Characterstics of connective tissue.
Examples of specialised connective tissue include 1 Bone 2 Cartilage 3 Both 1 2 4 Muscle. However muscle tissue is a separate entity like nervous tissue epithelial tissue etc with distinct functions. Kaneppeleqw and 2 more users found this answer helpful.
Epithelial tissue connective tissue muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Hyaline fibrous and elastic cartilage. Bones are the major connective tissue that supports the entire body and protects the organs.
When mast cells encounter an allergen they release the chemical. The elly like Interior of an eye D. There are three types of cartilage.
Which of the following types of cartilage would be found on the ends of long bones. A flat sheath-like tendon that connects muscle to bone is known as. Cartilage and bones is the correct answer because this tissue supports or connects all other tissues of the body and provides internal support.
Cartilage is a type of supporting connective tissue. The layer of photoreceptors in the eye. D Tendon All of the other tissues are vascular.
Fibrous cartilage has many collagen fibers and is found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Connective tissue possess large amount of intercellular space filled with ground substance or matrix.
Cartilage is perhaps the most vascular tissue in the human body. Which of the following is not an example of a connective tissue. In the embryo bone begins as hyaline cartilage and later ossifies.
The cartilage that is located in the eardrum called the tympanic membrane is an example of elastic cartilage. This explains why the cartilage is damaged when exposed to extreme heat or cold. A Elastic connective tissue.
Dense irregular connective tissue. They are connected to each other by ligaments. The thyroid and pituitary are examples of which type of gland.
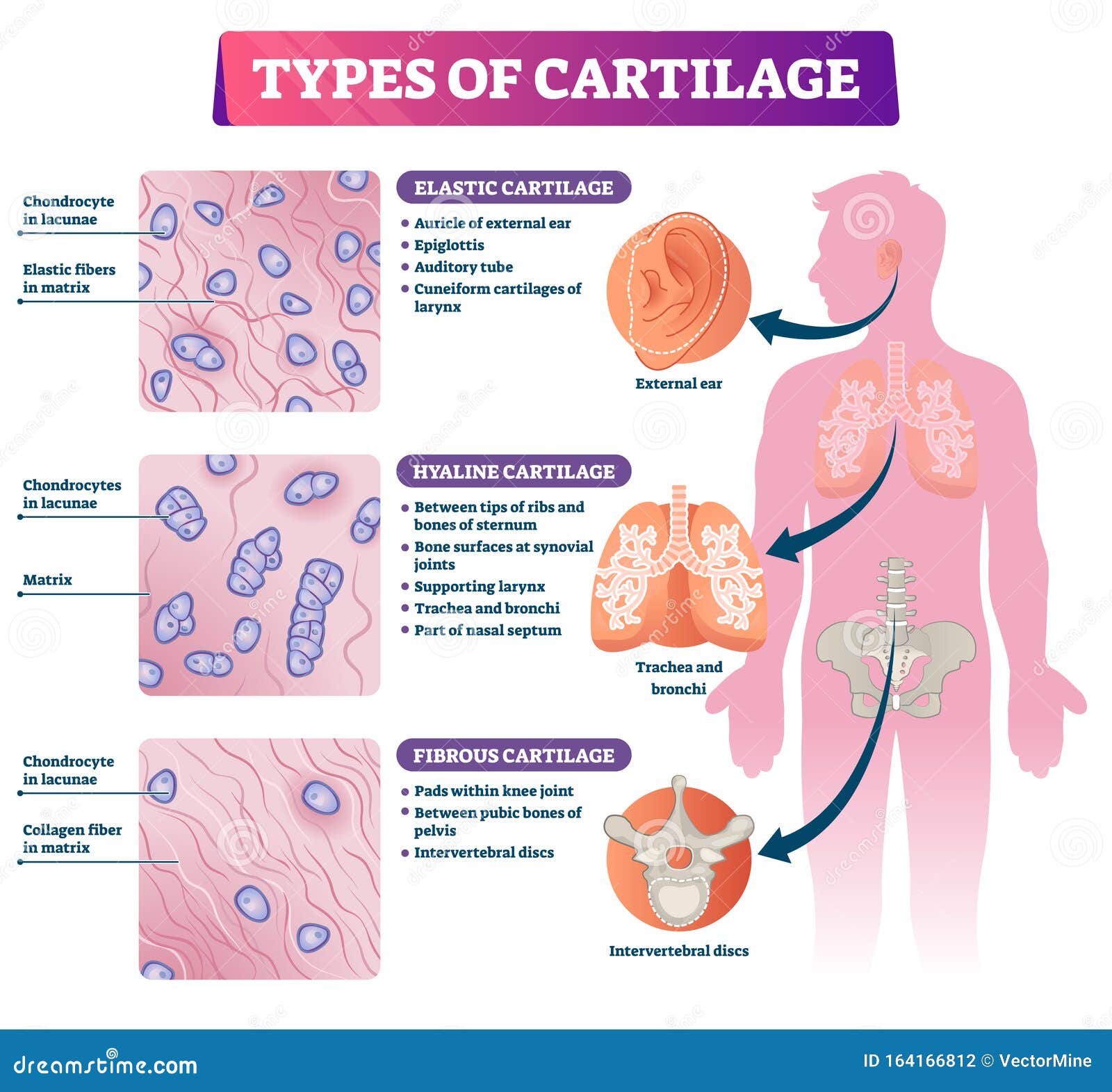
7 Types of Connective TissueCartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type and resembles glass. Has many cells and very little extracellular matrix C.
Fibrous cartilage has many collagen fibers and is found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis. Chondrogenesis is the process by which cartilage is formed from condensed mesenchymal cells. It provides protection against the injuries and entry of the pathogens.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. False Many researchers believe that one of the most basic factors in the aging process is the change in. Skin is the example of epithelial tissues it covers the inner dermal layers of the skin.
Which of the following is an example of dense connective tissue. Cartilage is present at the ends of the long bones which prevent the friction between the bones during movements. 100 4 ratings Transcribed image text.
Areolar connective tissue 2. Has many blood vessels D. B It is found in elderly females.
Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type and resembles glass. Hyaline fibrous and elastic cartilage. TF The most prevalent types of cells in areolar connective tissue are fibroblasts and macrophages.
TF The terms osteon and haversian system are synonymous. Cartilage is a semi-rigid but flexible avascular connective tissue found at various sites within the body. Covers internal and external surfaces of the body B.
Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and. Which of the following tissues has poor blood supply. There are three types of cartilage.
Bone and cartilage are grouped under skeletal tissue a category of specialized connective tissue. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function. Blood is a vascular tissue also categorised under specialized connective tissue.
A Areolar tissue b Bone c Reticular d Tendon. C It is found in teenage females. A tissue is a group of cells in close proximity organized to perform one or more specific functions.
In the embryo bone begins as hyaline cartilage and later ossifies. Which of the following characteristics is NOT true of epithelium. It is sensitive to heat and cold because the extracellular matrix does not have a high tolerance for temperature changes.
With a pliable structure composed primarily of water this tissue type is also extremely tough. Examples of tubes include the cricoid cartilage and carina of the trachea the torus tubarius at the opening of the auditory tube and the auriclepinna of the ear. This tissue supports and connects the various body parts.
A It is found in any child under the age of six. Attached to underlying tissue by a basement membrane and has a free surface.

The Following Flow Chart Depicts The Different Types Of Connective Tissue And Basic Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Loose Connective Tissue

Types Of Cartilage Vector Illustration Labeled Educational Tissue Scheme Stock Vector Illustration Of Bone Cellular 164166812

The Functions Of Connective Tissue Include Binding Of Organs Support Physical Protection Immune Protection Mo Tissue Types Loose Connective Tissue Tissue
0 Comments